Alkene Structure Stability
Hydrogenation reaction usually occurs on alkene. First we need to see how the above two rules pertain to this family.
This is a useful tool because heats of hydrogenation can be measured very accurately.
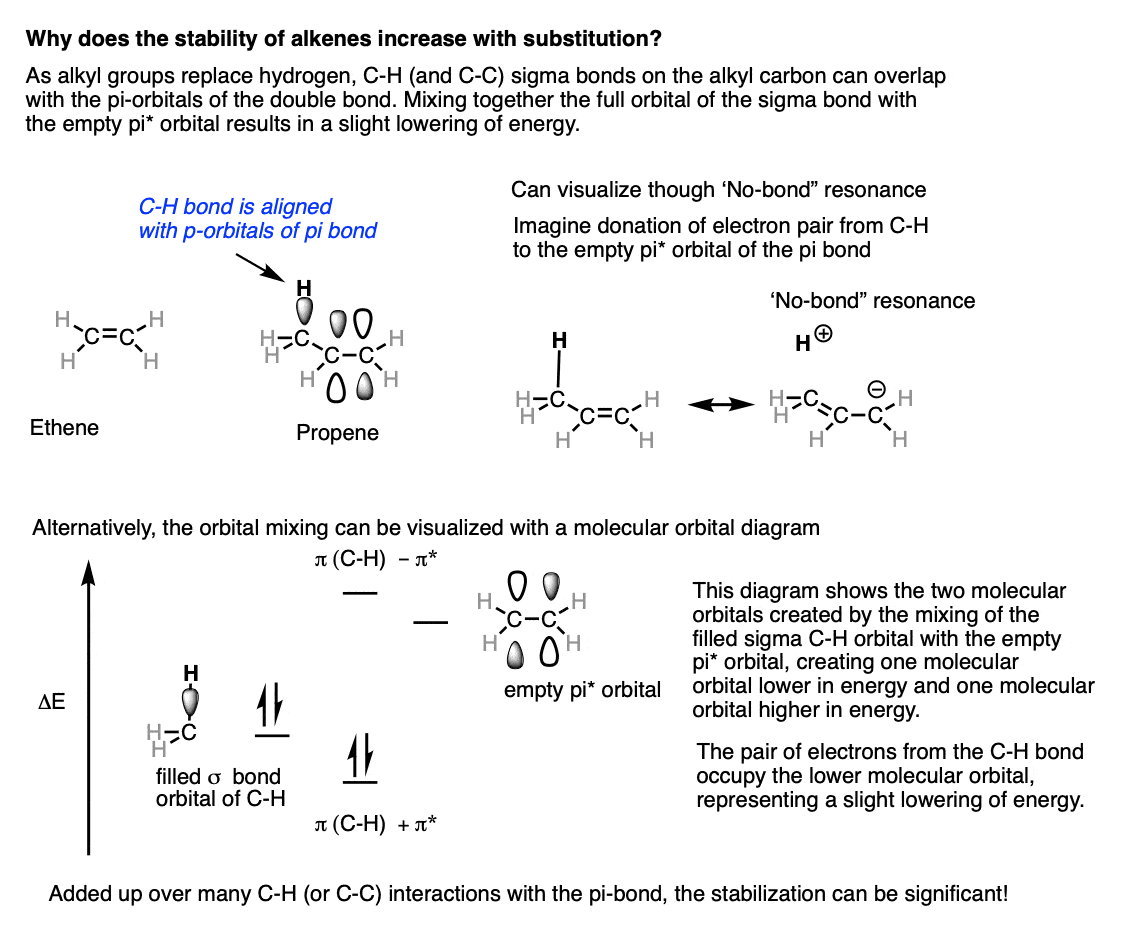
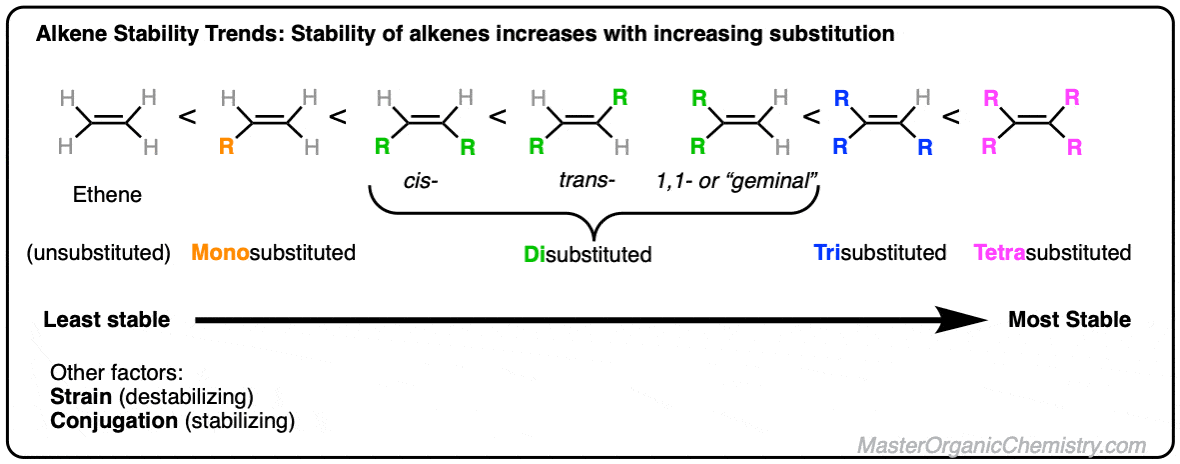
Alkene structure stability. The stability of alkene can be determined by measuring the amount of energy associated with the hydrogenation of the molecule. First the presence of alkyl groups directly attached to the double bond tends to stabilize the system. Alkenes - Structure Stability NomenclatureStructure Stability Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n if one alkene present unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum Hs possible per Ccontain fewer than maximum.
In Chapter 1 you learned that a pi bond represents the clouds of electrons that are above and below the. What is the general molecular formula for a cyclic alkene. Since the double bond is breaking in this reaction the energy released in hydrogenation is proportional to the energy in the double bond of the molecule.
H3CCH3 HH H3CH HCH3 cis-2-butene trans-2-butene H Catalyst at equilibrium the ratio is 76 trans and 24 cis. The carbon atoms in the double bond are. The pi bond is the weakest bond in an alkene so that is the bond that is going to break first.
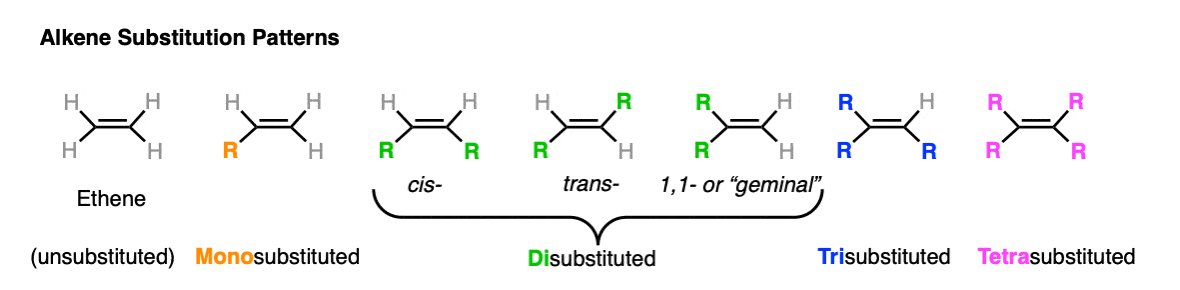
Alkenes are compounds that contain a carboncarbon double bond CC. We regard 1-butene as a monoalkylsubstituteddouble bond since it has one methyl group attached to the double bond. The stability of alkene can be determined by measuring the amount of energy associated with the hydrogenation of the molecule.
Since the double bond is breaking in this reaction the energy released in hydrogenation is proportional to the energy in the double bond of the molecule. Structure Nomenclature Stability and an Introduction to Reactivity. Alkene Structures Alkenes contain a double bond that is composed of one sigma and one pi bond between two carbon atoms.
DG -28 KJmol H3CCH3 HH H3CH HCH3 cis-2-butene trans-2-butene DHcombustion. There are 3 factors that influence alkene stability. The stability of an alkene can be determined by measuring the amount of energy associated with the hydrogenation of the molecule.
Quiz 1 This activity contains 12 questions. Degree of substitution ie. How many alkyl groups are attached to the CC.
-26855 KJmol -26822 KJmol 33 KJmol less energy is given off from trans isomer H3CCH3 HH H3CH HCH3 cis-2-butene trans-2-butene. The stability of an alkene is determined by the process of alkene hydrogenation that releases energy and provides stability to the double bond of an alkene Overview of Stability Of Alkenes An alkenes heat of hydrogenation leads to the stability of double bonds of carbon-carbon. The sigma bond has similar properties to those found in alkanes while the pi bond is more reactive.
The general formula and structure of. This video describes brief introduction of alkenes including some examples of important compounds from natural sources. More highly alkylated alkenes are more stable so tetra.
In contrast the 2-butenes have two methyl groups attached to the double bond. Since the double bond is breaking in this reaction the energy released in hydrogenation is proportional to the energy in the double bond of the molecule.
Alkene Stability Increases With Substitution Master Organic Chemistry

Alkene Stability Increases With Substitution Master Organic Chemistry

Pin On Alkene Reactions With Practice Problems

Alkenes Structure And Stability Chemistry Steps
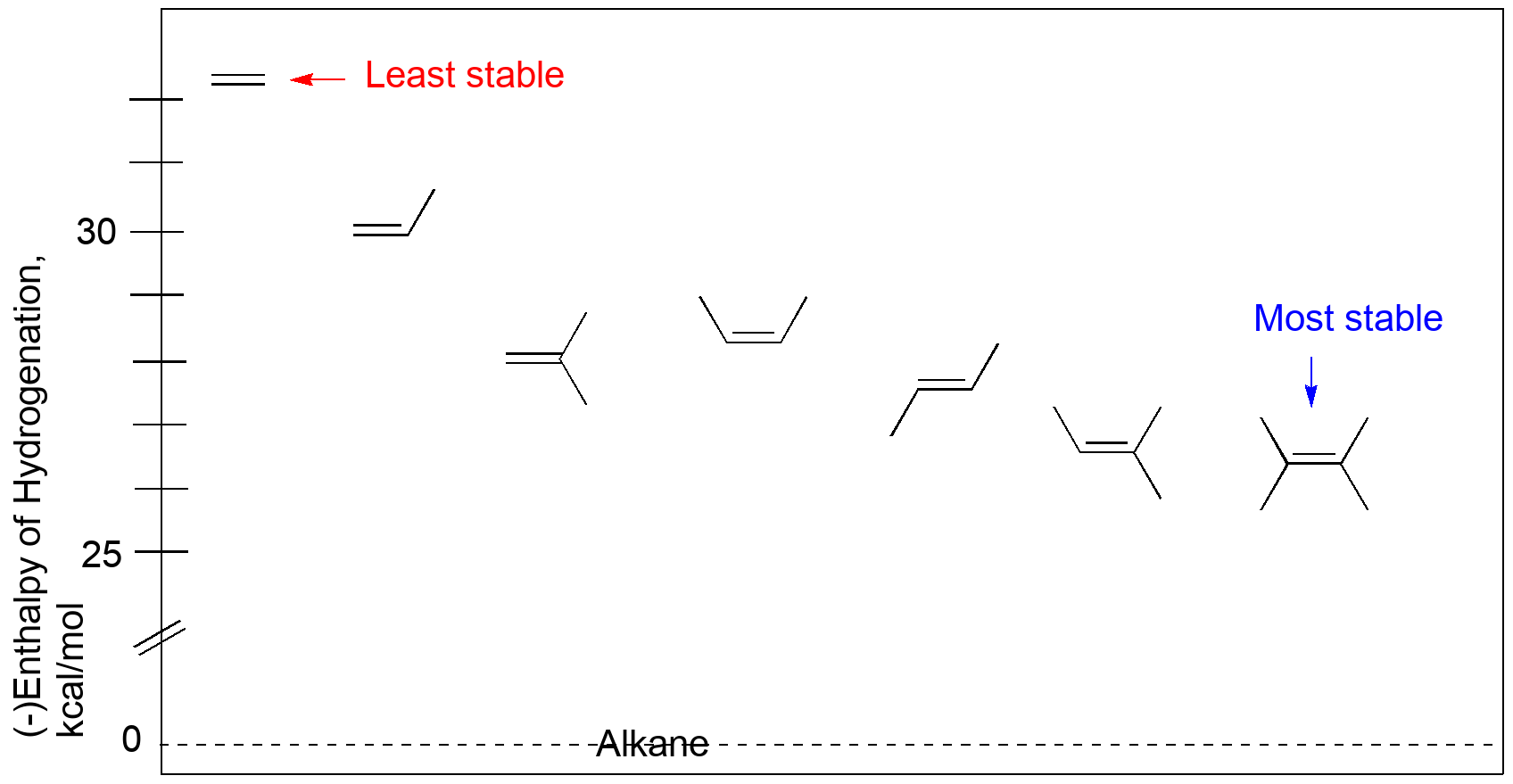
Alkene Stability And Substitution
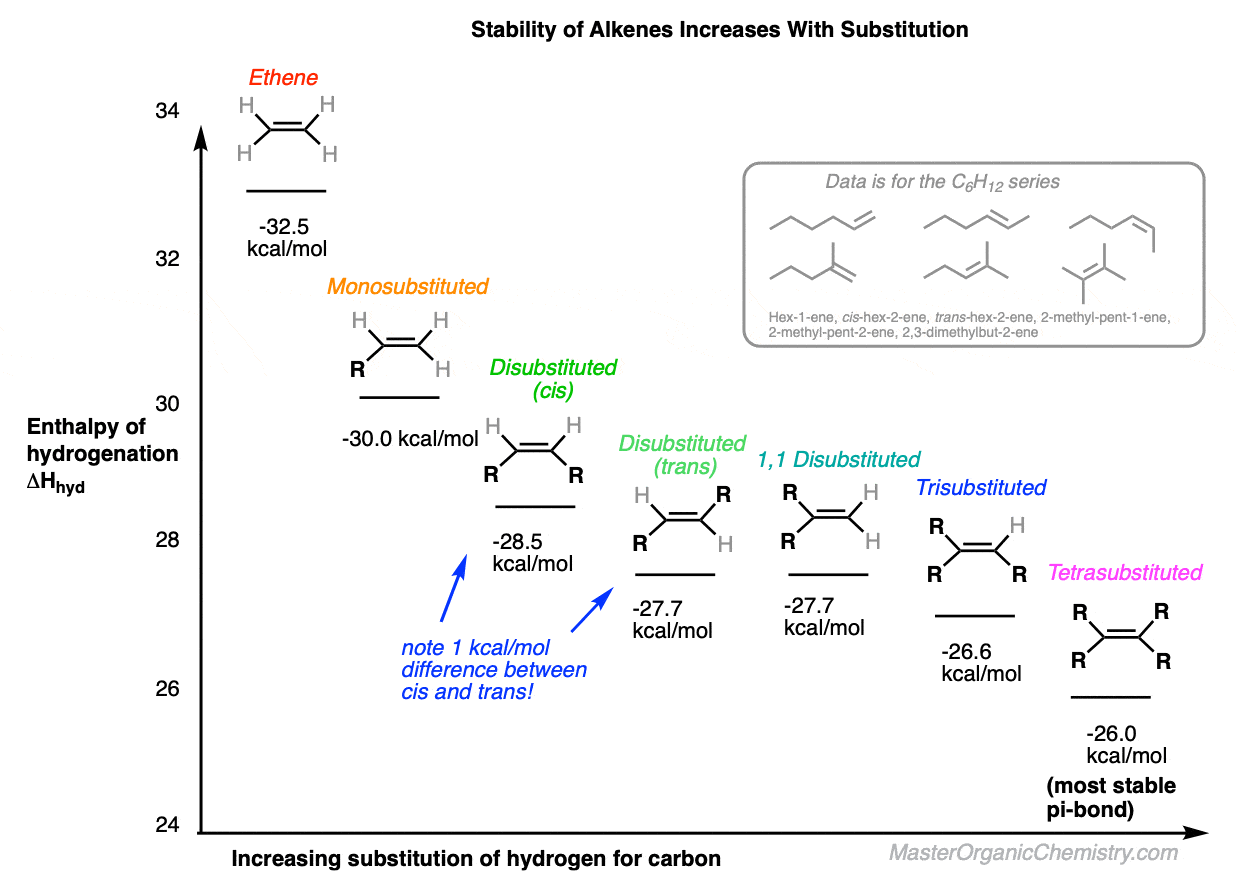
Alkene Stability Increases With Substitution Master Organic Chemistry
Alkene Stability Increases With Substitution Master Organic Chemistry



Post a Comment for "Alkene Structure Stability"